Controlling radiation in a high-frequency circuit or system can be challenging. As a result, RF absorber materials are frequently added to circuits to suppress or eliminate undesirable radiation coming from the circuit to the outside or to reduce the impact of radiated signals coming from outside the circuit (such as broadcast signals) on the functionality of the circuit.
What Is An RF Absorber?
Radio waves and microwaves are forms of electromagnetic energy generally described by the term Radio Frequency (RF). RF Waves /or/ Electromagnetic waves (EM Waves) can travel through anything either in air, solid material, or vacuum. RF/EM Waves can be transmitted, absorbed, or reflected depending on the sort of material.
Regulation of RF/EM disruptions and eliminating radiation field emissions are important to avoid interference. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can cause significant device disruption. It can cause computer malfunctions, produce false images, result in data corruption, and lower efficiency.
RF Shield Boxes /
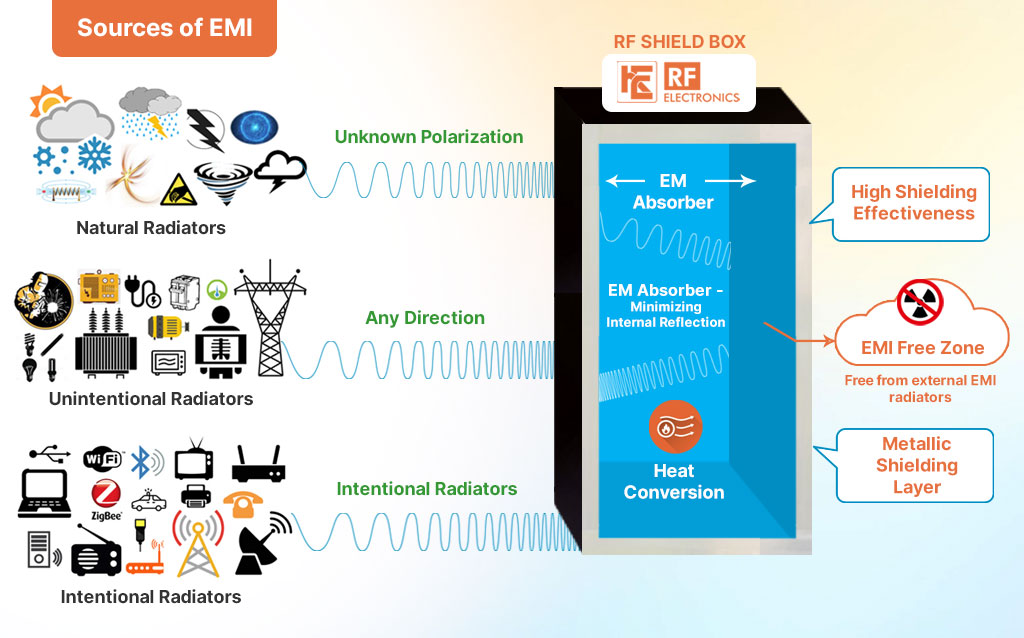
Anechoic Chambers are made from Metal Alloys which act as a mirror to any RF Signal Incident upon their surface creating unwanted Internal reflections / reverberation / multipaths / interference.
RF/Electromagnetic wave absorbers with the ability to absorb unwanted RF/electromagnetic waves are used to solve problems caused by electromagnetic interference in RF Shielded Test Enclosures.
Types of RF Absorbers
While taking into account the frequency range, attenuation levels, anticipated sounds, and other factors, the kind of absorber is matched with the specific range of applications, testing, and measuring settings, and the DUT (Device Under Testing). Types of RF Absorbers are:
Pyramidal Foam
In order to simulate a continual change in the dielectric, the absorber material is sliced into a pyramidal or geometrically tapering shape. The performance of pyramidal absorbers is inversely proportional to their size; for low-frequency performance, larger pyramids are needed. In contrast, a 4-inch absorber delivers negligible absorption below 1GHz but offers the same 50dB at 13GHz. Due to this size trade-off, pyramidal absorbers are very cheap yet limited to higher frequencies.
Ferrite Tiles
Materials with complex magnetic permeability equal (or nearly equal) to complex dielectric constant exhibit an impedance equal to that of "free space" and hence do not reflect radiated energy at normal incidence. Between 30MHz and 1GHz, ferrite tiles can produce 10dB to 25dB of absorption. Despite being relatively thin (around 0.26 inches), tiles can be heavy.
Hybrid
Hybrid
RF absorbers can combine the low-frequency benefits of ferrite tile and the high-frequency performance of broadband foam absorber by matching the impedance of the foam absorber and the ferrite. From 20MHz to 40GHz, hybrid absorbers deliver great performance. Both "open-cell" and "closed-cell" materials can be used to create hybrid absorbers.
Uses of RF Absorber
Primary uses of RF Absorbers are:
Attenuation Absorbers
Attenuation absorbers are primarily used to block noise signals from entering or leaving RF-shielded boxes, ensuring accurate testing and measurements as well as blocking the transmission of signals from a device inside the box without interfering with its surroundings.
Reflection Absorbers
In order to avoid interferences brought on by reflected signals, reflection absorbers are generally employed to absorb the energy of signal reflection inside the shielded region in any
RF testing equipment.
How An RF Absorber Works
RF Absorbers are specially shaped/chemically treated to allow for incoming RF energy to enter and then be transformed into heat resulting in a significant reduction of the reflected waves along the direction of echo.
For a good RF absorber, there should be negligible transmission and reflection. For achieving less transmission and reflection percentage, a material should have strong dielectric properties, permanent magnetic properties like high saturation magnetization, large magneto-crystalline anisotropy, high permeability, high resistivity, high Curie temperature, and low coercivity, etc.Properties such as high dielectric losses, high magnetic losses, and thermal stability are the desired attributes for EMI suppression applications.
Our RF Shield Boxes are deployed with high performance absorbers are constructed from a flexible material for life longevity with performance. For additional information, get in touch with RF Electronics!


